Page 28 - PlanWorld_1_2015_EN_high_0215
P. 28
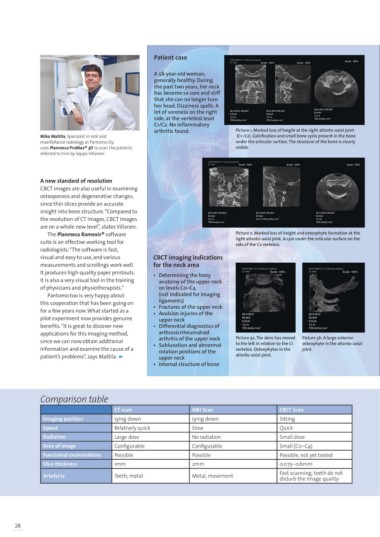
Mika Mattila, Specialist in oral and Patient case Picture 1. Marked loss of height at the right atlanto-axial joint
maxillofacial radiology at Pantomo Oy, (C1–C2). Calcification and small bone cysts present in the bone
uses Planmeca ProMax® 3D to scan the patients A 58-year-old woman, under the articular surface. The structure of the bone is clearly
referred to him by Seppo Villanen. generally healthy. During visible.
the past two years, her neck
has become so sore and stiff
that she can no longer turn
her head. Dizziness spells. A
lot of soreness on the right
side, at the vertebral level
C1/C2. No inflammatory
arthritis found.
A new standard of resolution Picture 2. Marked loss of height and osteophyte formation at the
CBCT images are also useful in examining right atlanto-axial joint. A cyst under the articular surface on the
osteoporosis and degenerative changes, side of the C2 vertebra.
since thin slices provide an accurate
insight into bone structure. “Compared to CBCT imaging indications Picture 3a. The dens has moved Picture 3b. A large anterior
the resolution of CT images, CBCT images for the neck area to the left in relation to the C1 osteophyte in the atlanto-axial
are on a whole new level”, states Villanen. vertebra. Osteophytes in the joint.
• Determining the bony atlanto-axial joint.
The Planmeca Romexis® software anatomy of the upper neck
suite is an effective working tool for on levels C0–C4
radiologists:“The software is fast, (not indicated for imaging
visual and easy to use, and various ligaments)
measurements and scrollings work well.
It produces high-quality paper printouts. • Fractures of the upper neck
It is also a very visual tool in the training • Avulsion injuries of the
of physicians and physiotherapists.”
upper neck
Pantomo too is very happy about • Differential diagnostics of
this cooperation that has been going on
for a few years now. What started as a arthrosis/rheumatoid
pilot experiment now provides genuine arthritis of the upper neck
benefits. “It is great to discover new • Subluxation and abnormal
applications for this imaging method, rotation positions of the
since we can now obtain additional upper neck
information and examine the cause of a • Internal structure of bone
patient’s problems”, says Mattila. ▰
Comparison table CT scan MRI Scan CBCT Scan
Lying down Lying down Sitting
Imaging position Relatively quick Slow Quick
Speed Large dose No radiation Small dose
Radiation Configurable Configurable Small (C0–C4)
Area of image Possible Possible Possible, not yet tested
Functional examinations 1mm 2mm 0.075–0.6mm
Slice thickness Fast scanning, teeth do not
Metal, movement disturb the image quality
Artefacts Teeth, metal
28